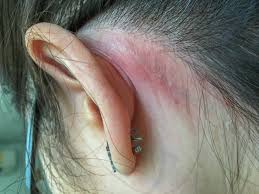
Celebrity Fan Web – Symptoms of metal allergies can range from mild to life-threatening for those with severe sensitivities. The most common symptoms appear on the skin, including itching, redness, and swelling after contact with metal.
The Science Behind Metal Allergies
Research indicates that these allergic reactions occur because certain metals, like nickel, chromium, or cobalt, do not have a complete set of electrons. Electrons in an atom orbit around the nucleus, and to achieve stability, an atom usually requires eight electrons in its outermost shell. However, nickel, for instance, has only two electrons in that shell. By releasing those two electrons, the atom stabilizes and acquires a positive charge. Thus, nickel in items like necklaces or buttons can release charged nickel ions that interact with the wearer’s skin.
Immune Response to Metals
Specifically, nickel ions bind to certain proteins in the skin. Since the body perceives these metal-bound proteins as “foreign,” it triggers an immune response. With repeated exposure to metals, immune cells can become increasingly sensitive. However, not everyone experiences sensitization, as this can be influenced by genetic factors and the skin’s protective barrier.
Manifestation of Symptoms
Symptoms of metal allergies may appear locally at the site of contact or may manifest throughout the body, depending on the extent of damage to the skin’s protective layer by the metal. Reactions can occur immediately after exposure, and if left untreated, they may spread to other areas of the body within hours or weeks.
Risks of Metal Allergies with Implants
It’s important to note that while rare, some individuals with metal allergies may also experience similar reactions to implanted objects, such as pacemakers, dentures, or joint replacements made from metal composites.
Managing Metal Allergies
Managing metal allergies involves a combination of avoidance and treatment. Here are some effective strategies:
Avoidance of Trigger Metals
The most straightforward way to prevent allergic reactions is to avoid contact with known metal allergens. This can include:
- Choosing jewelry made from hypoallergenic materials, such as titanium or surgical stainless steel.
- Using non-metal alternatives for items like buttons and fasteners.
- Being cautious with everyday items that may contain allergens, such as coins or keys.
Treatment Options
If a reaction does occur, several treatment options can help alleviate symptoms:
- Topical Corticosteroids: These creams or ointments can reduce inflammation and itching when applied to affected areas.
- Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines may help relieve itching and discomfort associated with allergic reactions.
- Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can soothe irritation and reduce swelling.
Seeking Medical Advice
For severe reactions or if you suspect you have a metal allergy, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Allergy testing can confirm specific sensitivities and guide appropriate management strategies.
“Also Read: Ways to Improve Your IoT Performance”
Conclusion
Understanding metal allergies is essential for those affected by this condition. By recognizing symptoms, avoiding triggers, and seeking proper treatment, individuals can effectively manage their allergies and minimize their impact on daily life. Awareness and proactive measures can lead to a more comfortable and healthier experience when interacting with metal items